“Slavery is the next thing to hell.” Harriet Tubman
I visited The Legacy Sites today in Montgomery, Alabama. The sites include the Legacy Museum, The National Memorial for Peace and Justice and the Freedom Monument Sculpture Park. I started with the Legacy Museum where no pictures were allowed but the stories contained in the modern building were powerful and sobering. The museum begins with enslavement, moves to racial terrorism, segregation and finally to mass incarceration. One fact that stood out was that from the years 1783 to 1861 enslavement increased 5 times over creating extraordinary wealth for some in the U.S.
In the wing covering mass incarceration, I was able to pick up the phone and listen to an inmate’s story while watching the video of the inmate. It mimicked sitting on the opposing side of glass and it was a powerful way to bring jail to life for me. Another section, asked the visitor to take the voter questionnaire in order to register to vote. The questions were impossible to answer and the intention of not being able to register to vote was loud and clear. For example some of the questions:
- How many seeds are in a watermelon?
- If a person charged with treason denied their guilt, how many persons must testify against them before they can be convicted?
- How many bubbles are in a bar of soap?
- How may a county seat be changed under the constitution of your state?
- Print a word that looks the same whether it is printed frontwards or backwards.
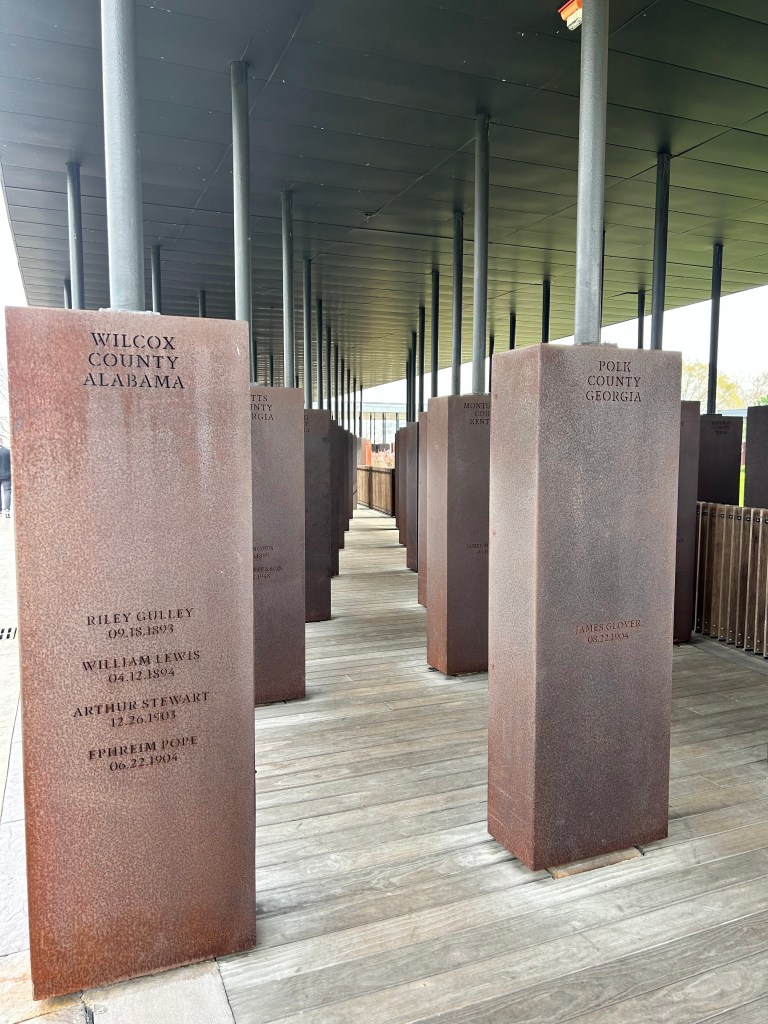
The last room in the building was a gallery with amazing art including two quilts from Gee’s Bend! The National Memorial for Peace and Justice was a six acre outdoor memorial dedicated to lynching. The grounds were pristine and the metal towers had the various locations and number of lynchings in that state or county. There were another set of metal structures that simulated coffins and a large water feature to honor the unnamed victims.
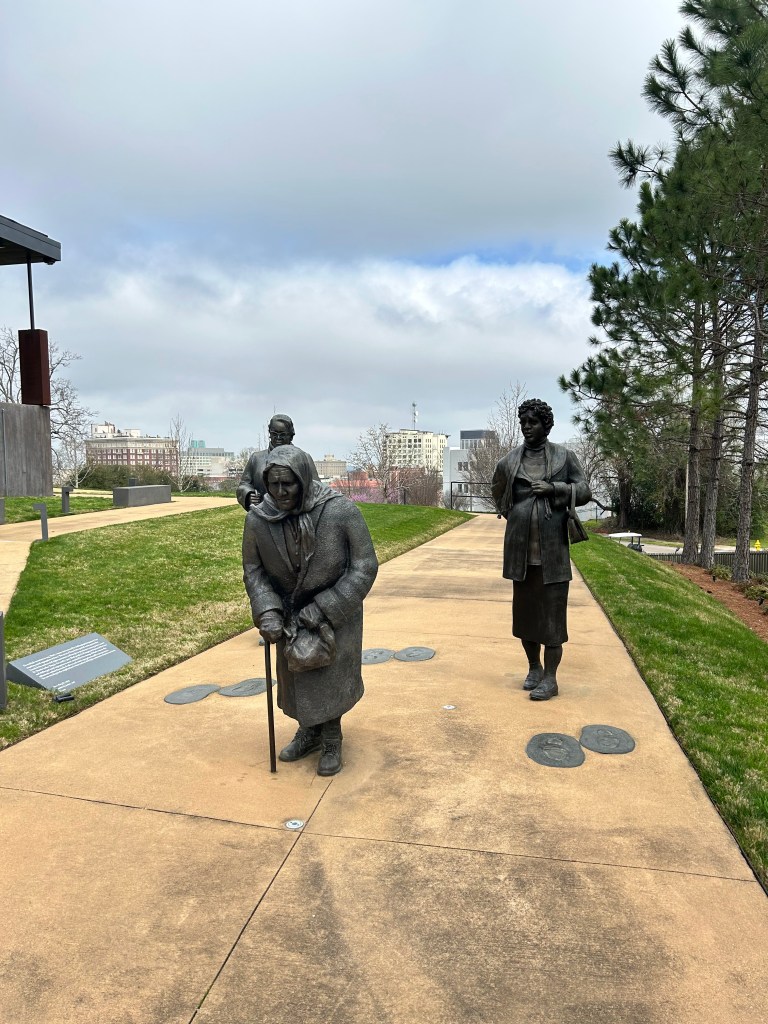
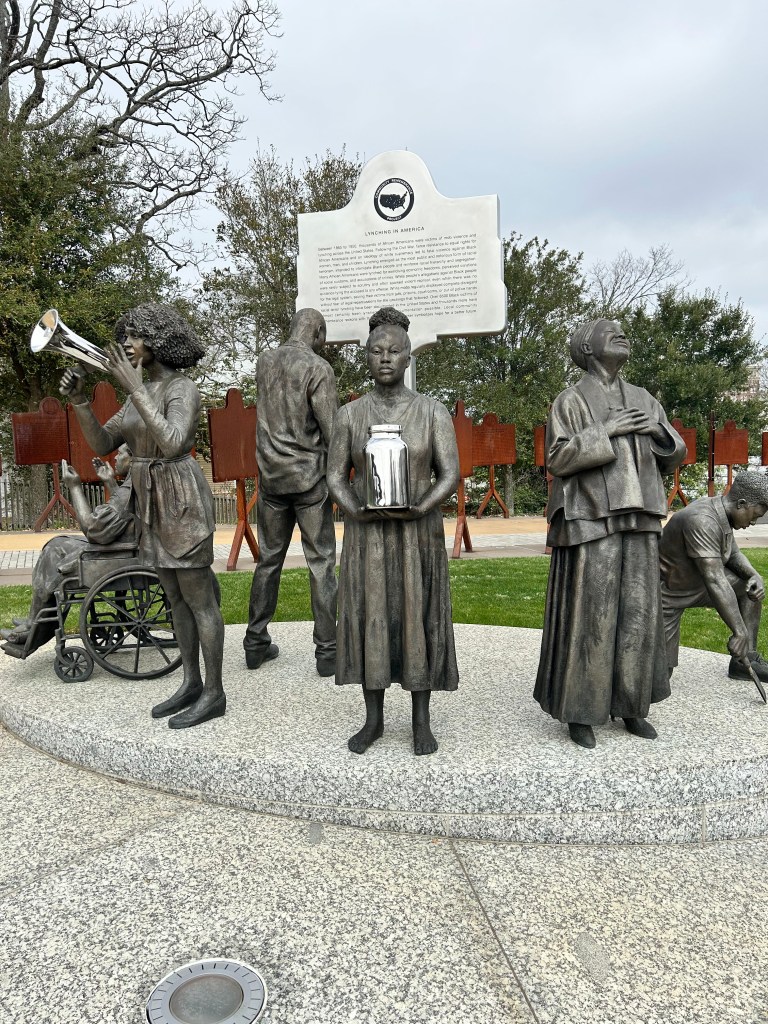
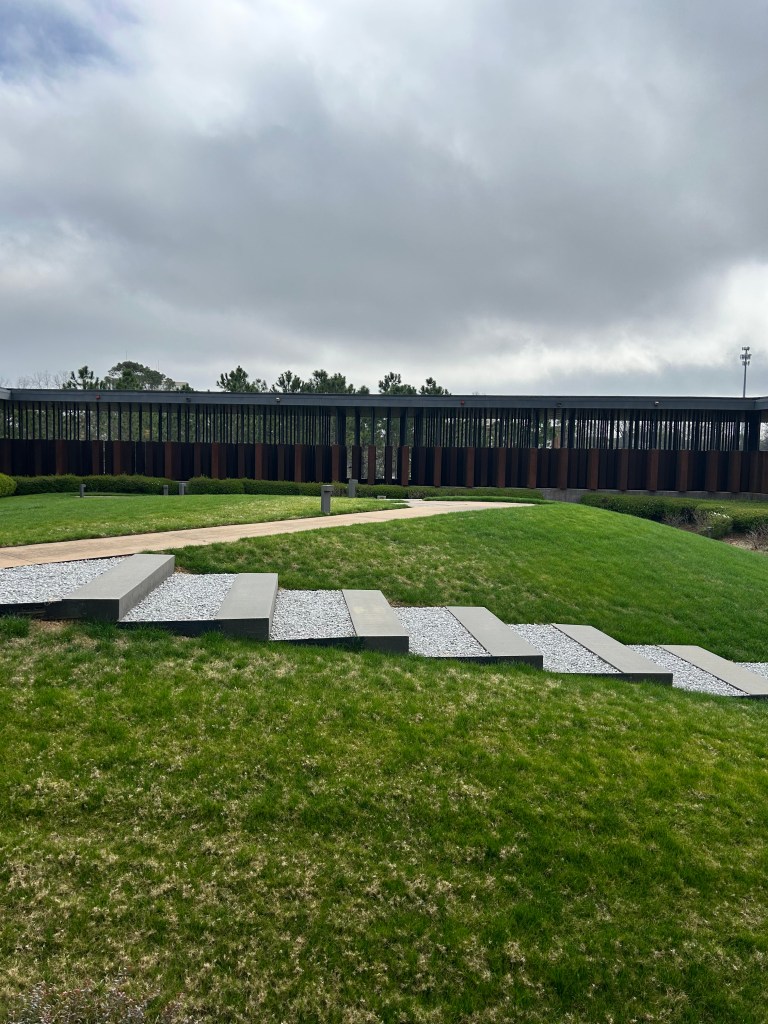
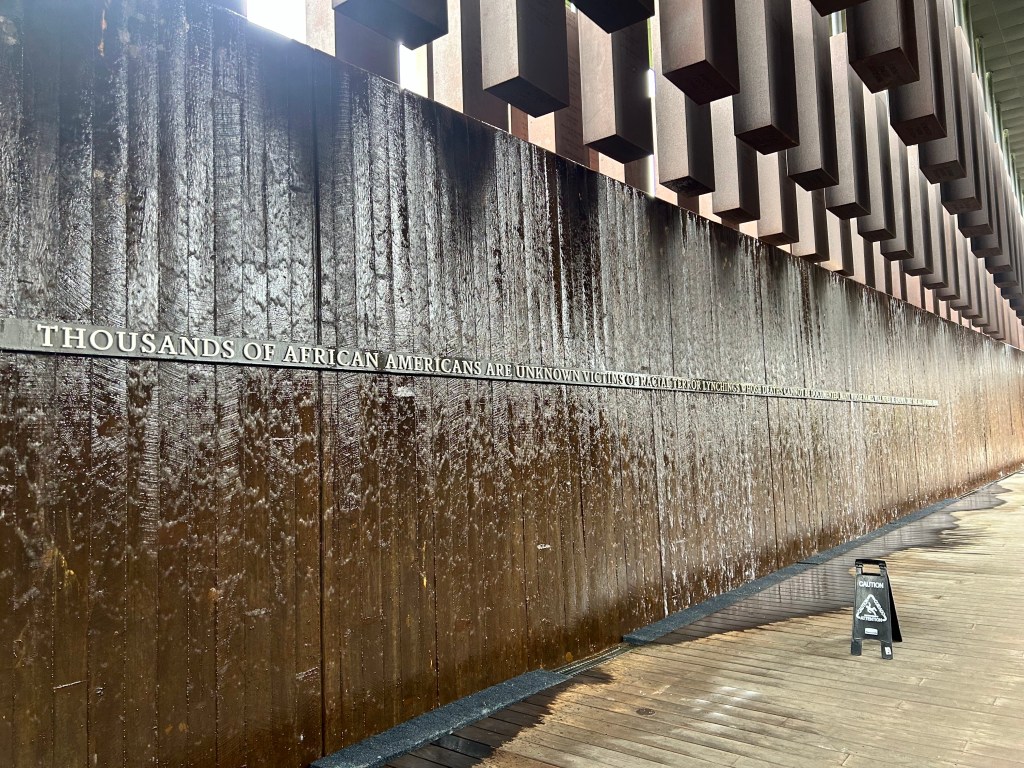
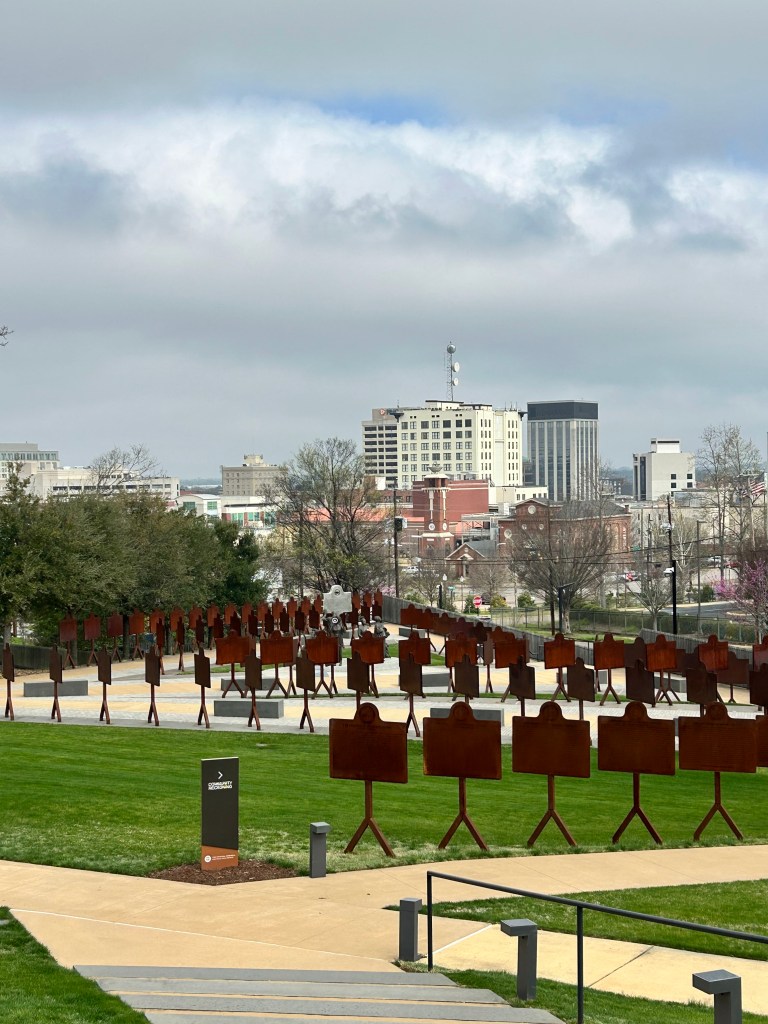
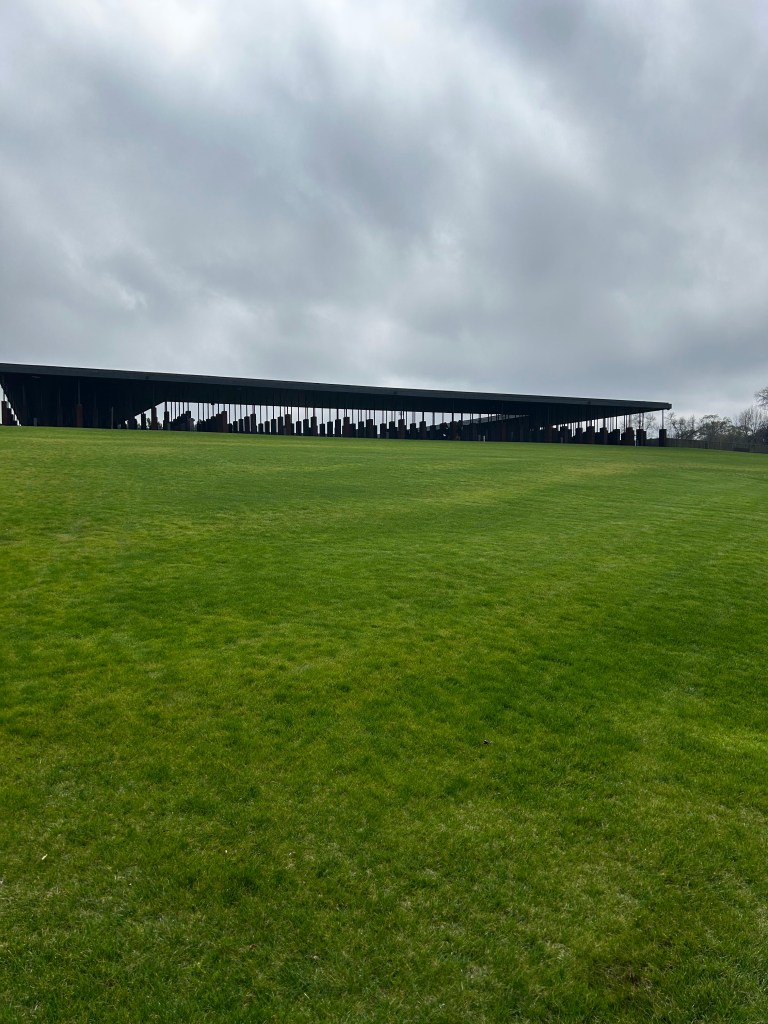










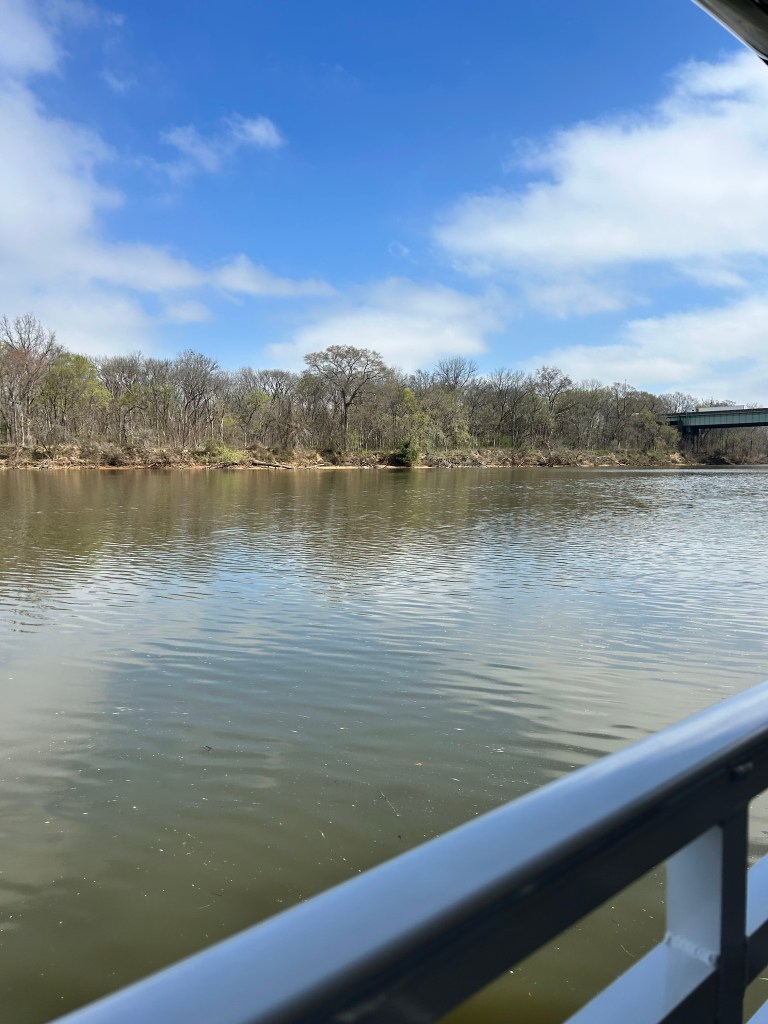
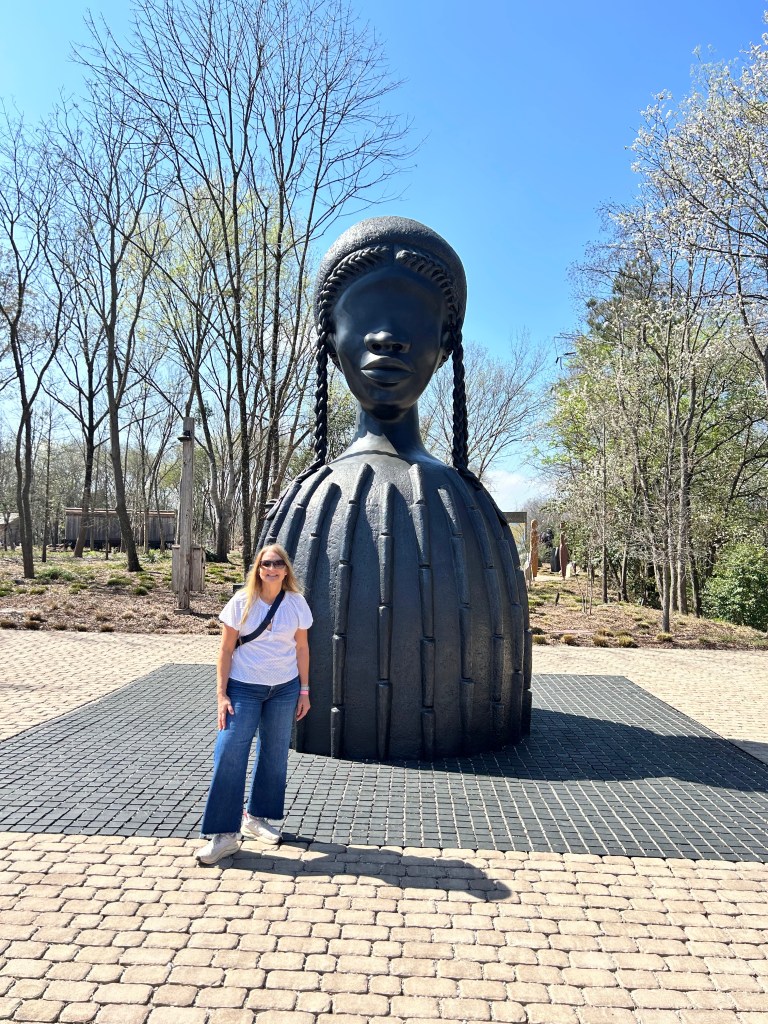
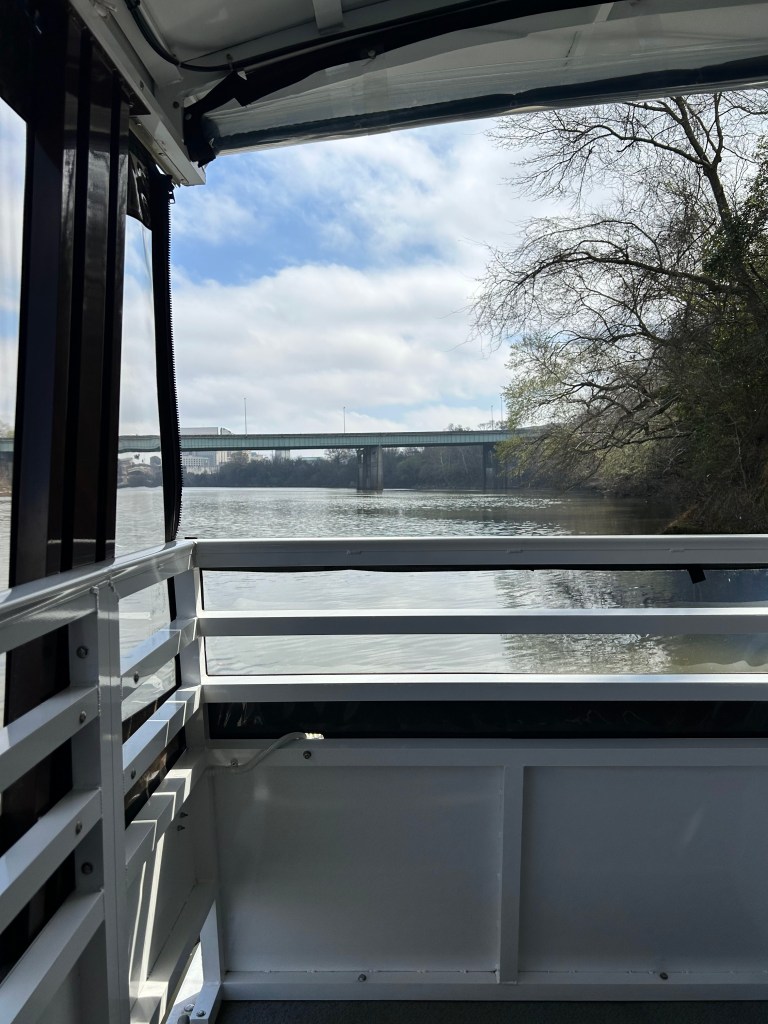
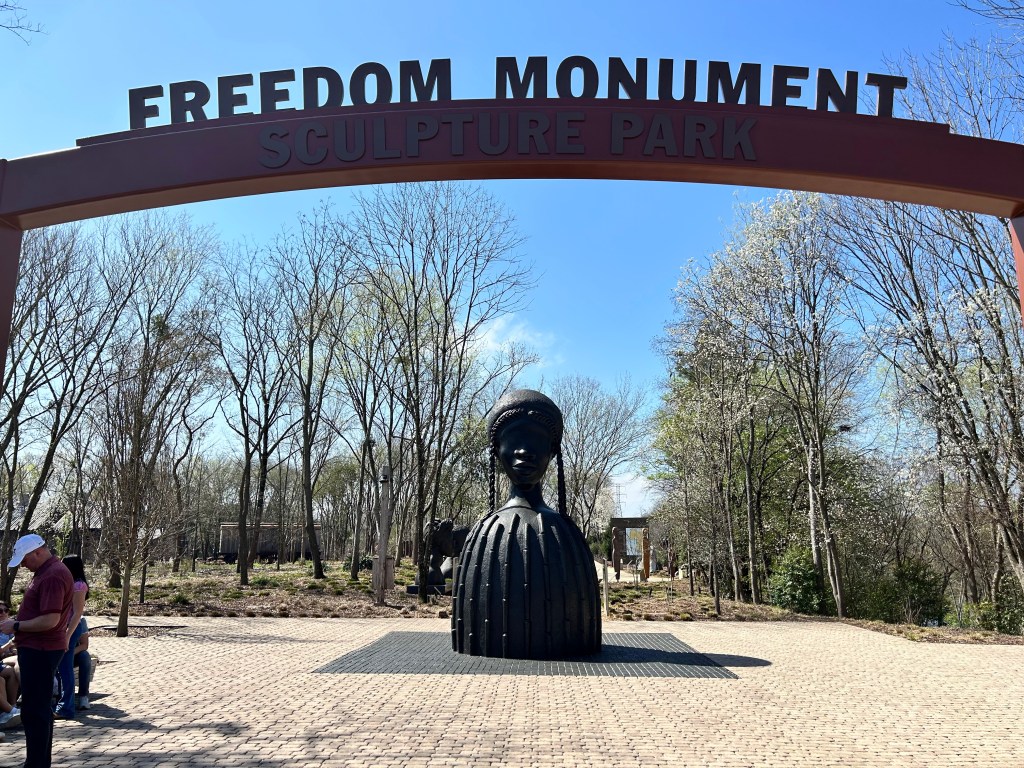
I took a boat ride down the Alabama River to the Freedom Monument Sculpture Park. This was the same way slaves were transported quickly to be sold or transported once sold. I landed at the 17 acre sculpture park that housed amazing sculptures, slave cabins, a railcar and holding paddocks. At the end of the loop was a memorial wall with thousands of names. Photos were limited to just the entry and the memorial. The art and sculptures were beautiful so you must visit yourself to see them!







Overall, I was impressed with Montgomery. It was clean and the old brick buildings and large, county buildings were beautiful. This museum was modern, clean and very thoughtfully mapped out. The metaphors were powerful and thought-provoking exhibits were well-done. Visitors undoubtedly walk away with a clear understanding of how institutional slavery has developed into a permanent hierarchy through our legal, political, religious and science institutions. Racism has been justified as necessary and enforced through violence and continues in our present day.